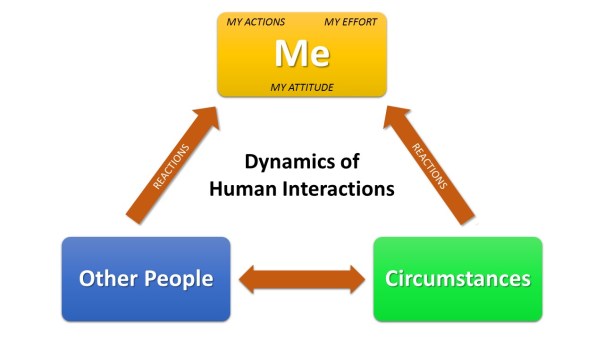
Accountability – the actions, attitude, and effort necessary to merge expectations with performance.
As we move forward with our discussion about leadership accountability, I must address two common myths that often send leaders down incorrect paths, or worse, make them appear to be hypocrites.
MYTH #1: Accountability is a team thing.

When I read books or listen to someone speak about leadership, I notice the theme of building positive, supportive, and unified teams is everywhere. Heck, I often write about the power of teams here on the TBLL Blog and fully endorse the benefits of building strong teams. However, when it comes to accountability, especially leadership accountability, it is not a team concept. The idea of “you hold me accountable and I, the leader, will hold you accountable” sounds great on paper or when said aloud, but there is one significant flaw in this logic. There is a complete lack of internal accountability being demonstrated where I recognize that I have the power to control both my expectations and my performance at all times. If I am relying on someone else to hold me accountable, am I really being accountable at all? The team accountability concept is based upon others controlling or setting my expectations for me. It means I am turning over the power of controlling my actions, attitude, and effort to say I need you to watch me and make sure I stay on the right path or do the right thing. Ultimately, the most significant issue with leadership accountability under this model becomes who is really leading, forging ahead, and setting the example?
MYTH #2: Accountability is something I, the leader, bestow upon other people.
 The second myth of accountability is that accountability is only something I do to other people. Specifically, the people that work on my squad or unit. If my view is that accountability is an external process of me holding others to my expectations or those of the department, then I am creating a culture of “them” and “they.” With this idea of accountability, I believe I must hold them accountable at all times and attempt to control their performance towards my expectations. This often comes across as micromanaging to those being led and to me it feels as if my entire job has become running around putting out fires all day. To those I am holding accountable, their perspective becomes one of contempt and I have now become part of the infamous “they.” The generic pronoun used to describe those higher in power within an organization when we feel there is not a choice in whatever matter is at hand. Ultimately, this style of accountability is only sustainable for as long as the leader can manage the energy to keep it up and are physically present around those they are “leading” to enforce their expectations. Once the leader becomes too tired to keep it up, they retract to the confines of their office to hide because they just cannot manage the level of effort required to constantly hold six to eight people constantly accountable. Worst of all is that none of those on the squad or unit have ever learned how to hold themselves accountable to these expectations because the boss has always done it for them.
The second myth of accountability is that accountability is only something I do to other people. Specifically, the people that work on my squad or unit. If my view is that accountability is an external process of me holding others to my expectations or those of the department, then I am creating a culture of “them” and “they.” With this idea of accountability, I believe I must hold them accountable at all times and attempt to control their performance towards my expectations. This often comes across as micromanaging to those being led and to me it feels as if my entire job has become running around putting out fires all day. To those I am holding accountable, their perspective becomes one of contempt and I have now become part of the infamous “they.” The generic pronoun used to describe those higher in power within an organization when we feel there is not a choice in whatever matter is at hand. Ultimately, this style of accountability is only sustainable for as long as the leader can manage the energy to keep it up and are physically present around those they are “leading” to enforce their expectations. Once the leader becomes too tired to keep it up, they retract to the confines of their office to hide because they just cannot manage the level of effort required to constantly hold six to eight people constantly accountable. Worst of all is that none of those on the squad or unit have ever learned how to hold themselves accountable to these expectations because the boss has always done it for them.
TRUTH: Accountability, especially leadership accountability, is all about me.
 The truth about leadership accountability is that it is all about ME. It starts with ME. It sustains with ME. It grows with ME. It can be ended by ME. The concept of anything in leadership being “all about me” is a colossal departure from 99.9% of what I read and hear about good leadership, but when it comes to leadership accountability it truly is controlling MY actions, MY attitude, and MY effort that dictate my application of accountability. Leadership accountability is an inside out process. It is through internal accountability that I set the proverbial bar or expectations. Those I am leading see what I am doing, how I am doing it, and most importantly I explain why I am doing what I am doing. As the example is set, then I have earned the right to set external expectations of those I am leading because they know that I am not and never would ask them to do something I am not doing or willing to do myself. In other words, I must exemplify accountability before I can ever expect it from those I lead – that is leadership accountability.
The truth about leadership accountability is that it is all about ME. It starts with ME. It sustains with ME. It grows with ME. It can be ended by ME. The concept of anything in leadership being “all about me” is a colossal departure from 99.9% of what I read and hear about good leadership, but when it comes to leadership accountability it truly is controlling MY actions, MY attitude, and MY effort that dictate my application of accountability. Leadership accountability is an inside out process. It is through internal accountability that I set the proverbial bar or expectations. Those I am leading see what I am doing, how I am doing it, and most importantly I explain why I am doing what I am doing. As the example is set, then I have earned the right to set external expectations of those I am leading because they know that I am not and never would ask them to do something I am not doing or willing to do myself. In other words, I must exemplify accountability before I can ever expect it from those I lead – that is leadership accountability.
Once the example of leadership accountability is set, then it begins to grow. In the next TBLL Blog, we will discuss how accountability grows through the leader’s example.
Questions to ponder . . .
- In my current leadership position, did I set the expectations first or set the example first?
- What are the benefits to be gained from exemplifying a solid foundation of leadership accountability?
- As a leader, do I control those I am leading or do I influence them?
The mission at Thin Blue Line of Leadership is to inspire law enforcement supervisors to be the best leaders they can be by providing positive leadership tactics and ideas. Positive leadership and creating a positive squad culture are on-going commitments that must be nurtured and developed over time. Thin Blue Line of Leadership is here to help.
Please do not hesitate to contact us if you have ideas to share or suggestions for improvement. Your thoughts or comments on this blog are always appreciated either below or on our Facebook page. You can also follow us on Twitter at @tbl_leadership.
Continue saving the world one call at a time and as always, LEAD ON!
*** Parts of this blog are paraphrased from the excellent book, QBQ: The Questions Behind the Question by John G. Miller.